What is an LED? Well, it's not complicated. Let me explain it in simple terms. An LED, or Light Emitting Diode, is a type of semiconductor that emits light when an electric current passes through it. You might have seen them in your everyday devices, like smartphones, TVs, or even traffic lights. But how exactly do they work? Let’s take a closer look.
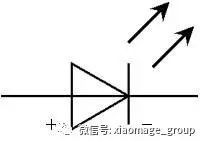
After looking at this image, you might think it doesn’t look like the LED you’ve seen in your electronics projects. That’s right—it’s not the actual LED itself, but rather its circuit symbol. The real LED has a specific structure and behavior. Let me show you what it looks like in practice.

As you can see, LEDs come in different colors, sizes, and shapes. It can be overwhelming to remember all of them. So, let’s break them down into categories for better understanding.
LEDs can be classified by color: red, green, blue, yellow, white, and more. They also vary in shape—some are cylindrical, others flat or shaped differently. There are also surface-mount (SMD) types, which are used in modern electronics.
For example, inline LEDs can be 3mm or 5mm in diameter, while SMD LEDs come in packages like 0603, 0805, 1206, and 2835. These are commonly used in PCBs and other compact designs.
Additionally, LEDs can be categorized by power: high-power ones used for general lighting, and low-power ones used as indicators on electronic boards.
Now, let’s talk about how to actually use a low-power LED, such as a 3mm red one. To use it properly, you need to understand its characteristics. Here’s a sample datasheet for a red inline 3mm LED:
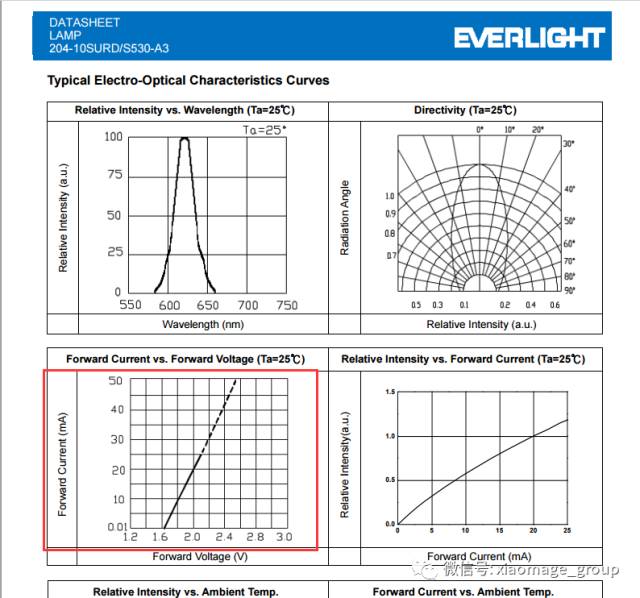
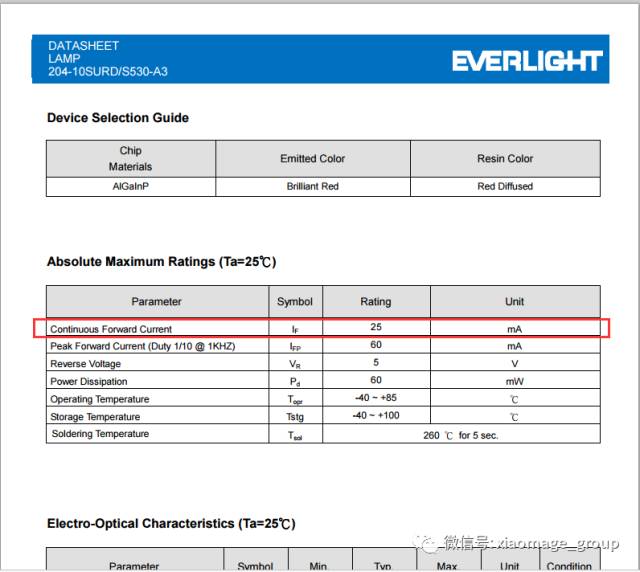
From the data sheet, we can see that the LED has a forward voltage of around 1.6V to 2.1V and a maximum continuous current of 25mA. If we connect it directly to a 5V power supply, it will draw too much current and burn out. That’s why we need a current-limiting resistor.
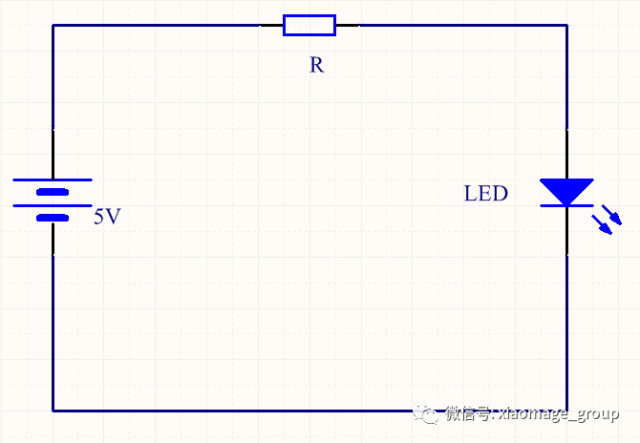
This is the classic LED circuit with a resistor. The resistor limits the current flowing through the LED, protecting it from damage. The formula to calculate the resistor value is: R = (V_supply - V_LED) / I_LED.
For example, if the supply is 5V, the LED forward voltage is 2.1V, and the desired current is 10mA, the resistor should be approximately 290Ω.
Now, let’s see how to use LEDs as indicators. For a power indicator, you can simply connect the LED in series with a resistor to the power supply. When the system is on, the LED lights up.
For a running indicator on a board, you can use a microcontroller to control the LED’s on/off state. Here’s a simple circuit:
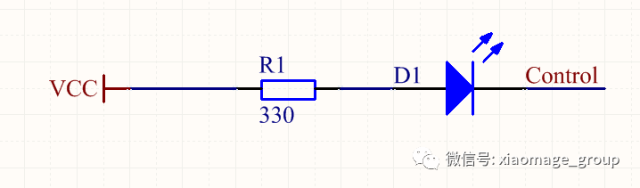
By toggling the input signal, you can make the LED blink. The blinking speed depends on the timing of the high and low signals.
That’s it! Now you know how to choose, use, and protect LEDs in your circuits. Whether you're building a simple project or a complex system, LEDs are an essential component. Try it yourself and see how easy it is to bring light to your electronics!
Mc4 Fuse Connector,Slocable Solar Pv Fuse,Mc4 Connector With Fuse,Mc4 Inline Fuse Connector
Sowell Electric CO., LTD. , https://www.sowellsolar.com