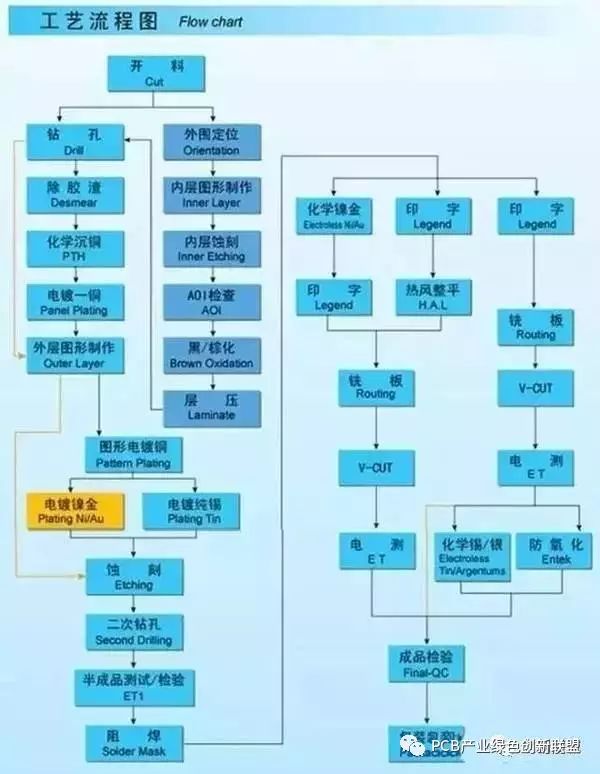
Cutting
Purpose: Based on the engineering data provided (MI), the large sheet is cut into smaller pieces that meet the customer’s specifications. This process ensures that the final product matches the required dimensions and quality standards.
Process: Large sheet material → Cutting board according to MI requirements → Seesaw cutting → Bevel edge grinding → Final inspection and exit of the board.
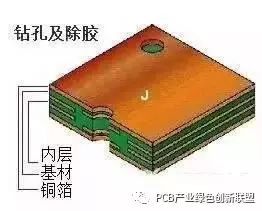
Drilling
Purpose: According to the engineering data, the necessary holes are drilled at the correct positions on the sheets of the required size, ensuring accurate alignment for subsequent processes.
Process: Stack pin placement → Upper plate setup → Drilling operation → Lower plate removal → Inspection and repair if needed.
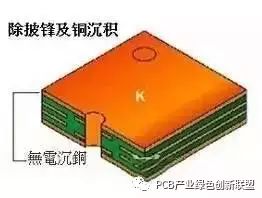
Copper Sink
Objective: A thin layer of copper is chemically deposited onto the walls of insulating holes to ensure good electrical conductivity and reliability in the final product.
Process: Surface roughening → Board hanging → Copper plating via automatic line → Lowering the board → Dipping in diluted sulfuric acid → Thick copper deposition.
Graphics Transfer
Purpose: The graphics transfer process involves transferring the image from the production film onto the board, ensuring precise pattern replication for further processing.
Process (Blue Oil): Board grinding → First-side printing → Drying → Second-side printing → Drying → Exposure → Shadowing → Final inspection. (Process - Dry Film): Board preparation → Lamination → Standing → Image exposure → Development → Shadowing → Inspection.
Graphic Plating
Purpose: Graphic plating is used to deposit a layer of copper to the desired thickness and apply a layer of gold or tin on the exposed copper areas or line walls, improving conductivity and corrosion resistance.
Process: Board loading → Degreasing → Two water washes → Micro-etching → Water washing → Acid pickling → Copper plating → Water washing → Acid pickling → Tin plating → Water washing → Board unloading.
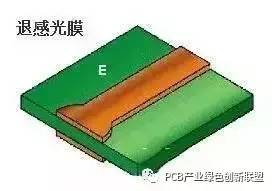
Stripping
Purpose: The anti-plating coating is removed using a sodium hydroxide solution to expose the non-line copper areas, preparing them for etching or other treatments.
Process (Water Film): Board insertion → Alkali soaking → Washing → Brushing → Machine passing. (Dry Film): Board placement → Machine passing.
Etching
Purpose: Etching is the chemical process used to remove unwanted copper from the non-line areas, leaving only the desired circuit patterns on the board.
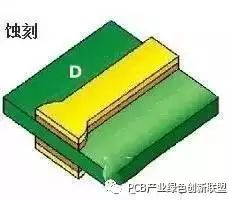
Green Oil
Purpose: Green oil is applied to protect the copper lines and prevent solder from adhering to them during the soldering process, ensuring clean and reliable connections.
Process: Board grinding → Photosensitive green oil printing → Plate fixing → Exposure → Shadowing. (Alternative method): Board grinding → First-side printing → Baking → Second-side printing → Baking.
Character Marking
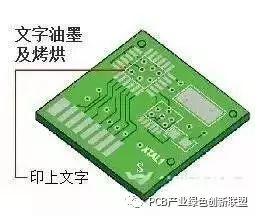
Purpose: Character marking adds visible and recognizable labels on the board, aiding in identification and traceability throughout the manufacturing and assembly process.
Process: After green oil application → Cooling → Network adjustment → Character printing → Final drying.
Gold Fingers
Purpose: Gold fingers are coated with a layer of nickel and gold to increase durability, wear resistance, and conductivity, especially for connectors and contact points.
Process: Board loading → Degreasing → Two water washes → Micro-etching → Two water washes → Acid pickling → Copper plating → Water washing → Nickel plating → Water washing → Gold plating → Final unloading.
Tin Plating (Solder Coating)
Purpose: Tin plating is used to coat the exposed copper areas not covered by solder resist, preventing oxidation and ensuring good solderability during assembly.
Process: Micro-etching → Air drying → Preheating → Rosin coating → Solder coating → Hot air leveling → Air cooling → Washing and drying.
Forming
Purpose: The forming process shapes the board according to the customer's design using methods like die stamping, CNC machining, or manual cutting. It includes organic enamel, beer board, hand-cut, and similar techniques.
Note: Data boards and beer boards offer high precision, while hand-cut boards are suitable for simpler shapes and lower accuracy requirements.
Testing
Objective: Electronic testing ensures complete detection of hidden defects such as open circuits or short circuits that may not be visible to the naked eye, enhancing product reliability.
Process: Mold loading → Board release → Testing → Qualified → FQC visual inspection → Unqualified → Repair → Re-test → Acceptable → Reject → Scrap.
Final Inspection
Purpose: A thorough visual inspection of the board’s appearance is conducted to identify and address minor defects, preventing faulty products from reaching the customer.
Workflow: Incoming materials → Data review → Visual inspection → Qualified → FQA random sampling → Qualified → Packaging → Unqualified → Processing → Final check.
Rubber Insulated Wires,Rubber Cable,Rubber Coated Wire,Rubber Earth Wire
HENAN QIFAN ELECTRIC CO., LTD. , https://www.hnqifancable.com