With the rapid advancement of power electronics and semiconductor technology, various types of power electronics applications are beginning to require specialized, professional semiconductor switching devices to achieve a win-win situation in cost and performance. Field-stop (FS) IGBTs further reduce saturation voltage drop and switching losses compared to conventional non-punch-through (NPT) IGBTs. In addition, the relatively new technology of integrating anti-parallel diodes on IGBT dies using anode short-circuit (SA) technology makes FS IGBTs ideal for soft-switching power conversion applications.
Field cut-off anode short-circuit trench IGBT vs. NPT IGBT
Although NPT (non-punch-through) IGBTs increase switching speed by reducing minority carrier injection during turn-off transition and increasing recombination rate, they are not suitable for some high-power applications due to their high VCE(sat) because of their n- The substrate must be lightly doped, with the result that a thicker substrate is required to maintain the electric field during the off state, as shown in Figure 1(a). The thickness of the -n-substrate is the main factor determining the saturation voltage drop in the IGBT.
The "n" type doped field stop layer (shown in Figure 1(b)) between the "n-" drift layer and the "p+" collector of a conventional NPT IGBT significantly improves the performance of the IGBT. This is the concept of a field stop IGBT. In FS IGBTs, the electric field sharply weakens in the field stop layer and gradually decreases in the "n-" drift layer. Therefore, the thickness and saturation pressure drop of the "n-" drift layer are significantly improved. The channel gate structure also improves the saturation voltage drop. In addition, the field stop layer of the FS IGBT accelerates the majority carrier recombination at the turn-off instant, so its tail current is much smaller than that of the NPT or PT IGBT. This reduces the switching loss and the turn-off energy Eoff.
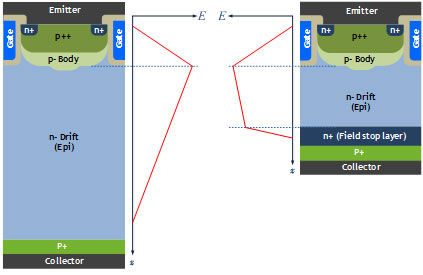
Figure 1: NPT IGBT (left) and field-off IGBT (right)
At the same time, a new concept emerged - the anode short-circuit IGBT (SA IGBT): it allows the body diode to be embedded in the IGBT as a MOSFET. Figure 2 shows the basic structure of the field stop channel anode short circuit (FS T SA) IGBT concept, where the "n+" collector is adjacent to the field stop layer as the cathode of the PN diode and the "p+" collector layer acts as the FS T The common collector of the IGBT.
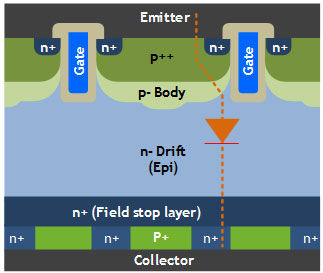
Figure 2: Sectional view of the FS SA T IGBT
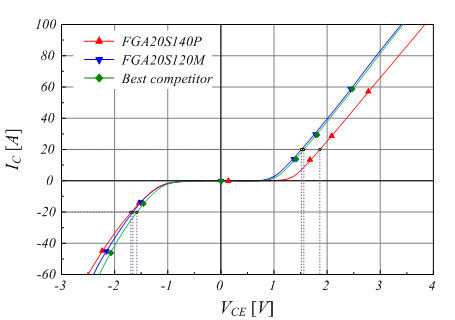
Figure 3: Comparison of typical output characteristics
Zhejiang Synmot Electrical Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.synmot-electrical.com