The commercial aviation industry has largely accepted lightweight materials because we always like to make short-lived comparative choices (such as airline tickets) when purchasing tickets, which makes airlines need to improve their fuel economy. Thereby saving costs. The key reason for the early adoption of additive manufacturing (AM) in the aerospace industry was lightweight implementation. Specifically, in the aerospace field, there are four main ways to achieve lightweighting through 3D printing through structural design: hollow interlayer/thin-wall reinforced structure, hollow lattice structure, integrated structure realization, and heterogeneous topology optimization structure.
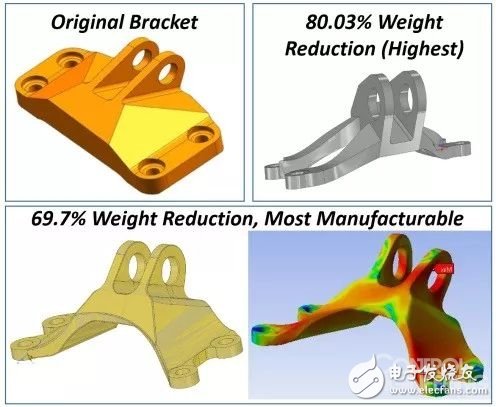
But when it comes to the automotive industry, because of the high cost of current 3D printing for manufacturing, it is easy to doubt the potential of it to implement light vehicles for consumers. Recently, General Motors (GM) and Autodesk have created a seat bracket made of additive, claiming a 40% weight reduction, although the cost may not be suitable for the current application, it may take several years to be around the world. Launched a car that uses these brackets. Nonetheless, this is a promising development as it represents a step in the direction of additive manufacturing to the current efforts to penetrate - mass production.
The Ford Model T was first launched in 1907 and weighed about one-third of the current Tesla 3 model. Today, our cars are much heavier than they were a century ago. In fact, over the past two decades, on average, the weight of a given class (car, SUV, truck) has barely changed. Of course, consumers do not consider too much about the weight of the car when choosing a car, but pay more attention to performance, safety and function, but the weight of the car can not be ignored.
For more than 100 years, engineers have been exploring lightweight strategies. As additive manufacturing technology enters the production floor and further evaluates the four strategies of lightweighting from additive manufacturing, it can gain a deeper understanding of the future possibilities in this area.
Lightweight is most likely to be considered a material selection issue. Every material science engineer and most mechanical engineers place a strong emphasis on the relationship between materials and lightweight, and materials can be selected to achieve certain performance goals (strength, modulus, etc.) related to material density. When making material selection, first consider the lowest density material that meets all design requirements. Of course, other factors such as manufacturability (such as ductility) and cost will also play a role and may dominate the selection considerations.
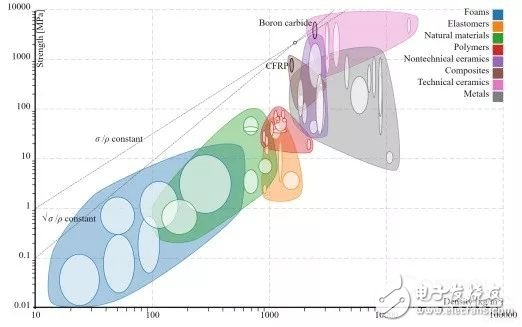
Figure: Ashby plot of material and strength
Weight is the result of a combination of materials and structures, and once the material is selected, a further opportunity is to use the design to reduce the overall weight of the structure. Significant weight reduction through "structural" optimization, including by removing materials (especially through topology optimization), or by integrating the structure into fewer parts through an integrated structure.
Dot matrix structures or porous materials reduce the weight of the product at the "micro" level. For example, in bone implants, the stiffness of the bone is mimicked by local variations, not only for the purpose of weight reduction, but also makes it easier for the human body to "accept" such implants. However, it is not easy to achieve weight reduction through lattice cell structure. 3D Science Valley introduces the points that need to be paid attention to in continuous modeling in the article "Six Challenges of 3D Print Cell Structure Modeling" and how to To achieve accurate, uniform and isotropic materials in honeycomb materials, how to pay attention to the mechanical properties of the "macro" level of the shape design on the "micro" level of cell structure, how to pay attention to the impact of dimensional tolerances, and the direction of printing The effect of mechanical properties.
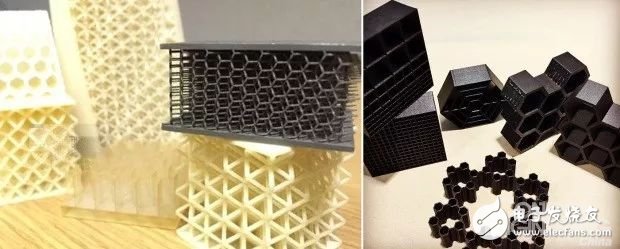
In the article "Four Types of Cell Modeling", 3D Science Valley has shared several common structures in detail, including honeycomb structure, open cell foam, closed cell foam, and lattice structure.
In the lightweight context, versatility represents the opportunity to use materials and structures in a way that ultimately offsets the number of components and assembly equipment such as fasteners, thereby achieving lightweight. The concept of versatility is derived from the wing schematic in the 2016 review article by Schaedler and Carter, as shown. The core function of the wing is to generate lift. However, from a lightweight point of view, we are interested in the structure that makes up the wing. These structures must be resilient under all expected environmental conditions, but they can also be refined by optimizing the position of the center of gravity and/or thermal management or energy storage. Through the design process, these local structures need to be combined with continuous topologies such as the skin of the wings and internal pipes.
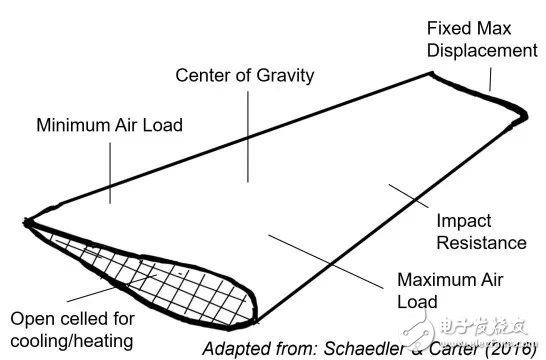
Figure: The wing schematic in the 2016 review article by Schaedler and Carter
In the era of multi-material, high design fidelity, how do we best optimize the materials together and achieve better structure and function in the way of additive manufacturing? In addition to these strategies, drawing inspiration from nature is an effective method. In the lighter context, additive manufacturing will help achieve lightweight implementation on the one hand, and the current material selection and cost constraints remain the challenge of entering mass production. But these challenges will not continue for a decade, whether it is turning our technology into lighter vehicles on our roads or in engineering, and the potential for additive manufacturing is working.
Ningbo Xingchuangzhi Electric Appliance Co.,Ltd. , https://www.xingchuangzhi.com