Popular Science | What Are the Effects of Different Light Sources on Health?
Release date: 2017-10-26 Source: Foreign station
The impact of lighting on health is not only about the spectral components of the light source, but also includes electromagnetic radiation, noise, glare, flicker, and the safety of the luminaire. Not all wavelengths in the spectrum are harmful, and many of these light sources have been part of our daily lives for years.

All illumination sources contain red, green, and blue components. The blue light from these sources has always existed and will continue to be a part of our environment. However, by understanding how to avoid and use them properly, we can minimize any potential harm from blue light.
This article provides scientific insights into artificial light sources, helping you better understand their effects on health. Let’s explore the different types of lighting and their impacts.
Incandescent Lamps
The full spectrum is shown in the figure below. Incandescent lamps have been widely used in various lighting applications over the years.
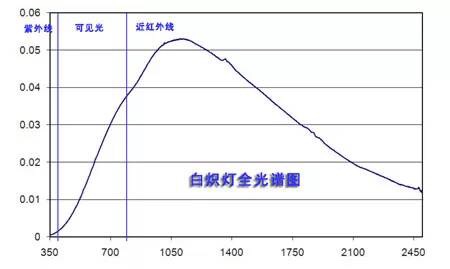
Health Effects of Incandescent Light
1. UV-A content is very low, so its effect on health is negligible.
2. UV-B content is almost non-existent.
3. The blue light content is low, making it less stimulating to the eyes. It is considered one of the safest options for indoor lighting.
4. High near-infrared content may cause dry skin and wrinkles over time. The high surface temperature also poses a risk of burns.
Due to low efficiency and high energy consumption, incandescent lamps are being phased out. From a health perspective, they pose minimal risks.
Halogen Lamps
The full spectrum is shown in the figure below. Halogen lamps are commonly used in spotlight applications indoors.
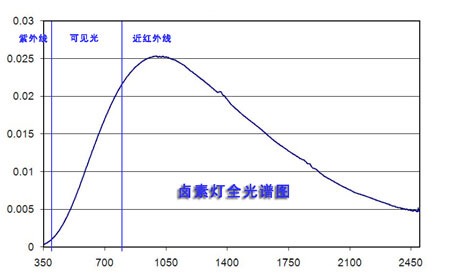
Health Effects of Halogen Light
1. UV-A levels are very low, so their health impact is negligible.
2. UV-B content is minimal and not significant.
3. Blue light content is low, making it relatively safe for indoor use.
4. High near-infrared content may lead to dry skin and wrinkles. The high surface temperature can also cause burns.
Like incandescent lamps, halogen lamps are inefficient and energy-consuming, leading to their gradual phase-out. Their health impact is minimal when used appropriately.
Metal Halide Lamps
The full spectrum is shown in the figure below. These lamps are often used in commercial settings such as jewelry and clothing stores.
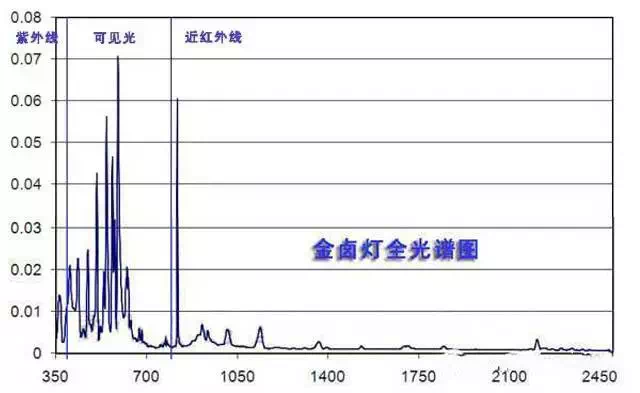
Health Effects of Metal Halide Light
1. UV-A content may affect health.
2. UV-B content is small and not significant.
3. High blue light content can damage the retina.
4. Medium infrared content may lead to dry skin and wrinkles. High surface temperatures can cause burns.
These lamps are still widely used in commercial environments. They contain UV and IR rays, and high color temperature versions emit more blue light, which can be harmful to the eyes. Long-term exposure at close range may lead to skin spots.
Warning: Please ignore the image below if you're sensitive to beauty; it's just a reminder of what you might see in a store!

Before LEDs became popular, metal halide lamps were widely used due to their good lighting quality and color rendering. However, with the development of LED technology, many issues like UV and IR radiation have been resolved. Despite this, some LED lights with high color temperatures can emit more blue light than traditional lamps, increasing the risk to the retina.
Fluorescent Lamps
The full spectrum is shown in the figure below. Fluorescent lamps are among the most commonly used lighting solutions today.
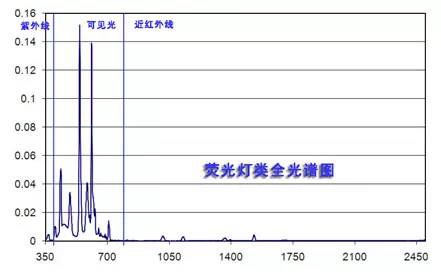
Health Effects of Fluorescent Light
1. UV-A content may have an effect on health.
2. UV-B content is small and can be ignored.
3. High blue light content may cause retinal damage.
4. Near-infrared content is minimal and its impact can be ignored.
Fluorescent lamps emit ultraviolet light that can penetrate the glass tube. Although high-quality lamps have lower UV leakage, poor-quality ones may emit higher levels. This is an important consideration when choosing fluorescent lighting.
Prolonged use of fluorescent lighting may damage the skin, causing it to turn red and lose moisture.
Studies show that the UV exposure from a day under fluorescent lights is similar to an hour in the sun. Therefore, it's crucial to ensure fluorescent lamps meet GB/T 20145-2006 standards before installation.
With the rise of LED technology, fluorescent lamps are gradually being replaced. While LEDs reduce UV exposure, they introduce new concerns related to blue light radiation.
LED Lighting
The full spectrum is shown in the figure below. LED lamps are now widely used and their application is growing rapidly.
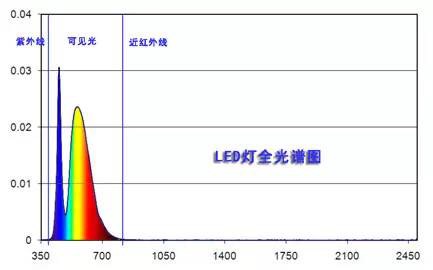
Health Effects of LED Light
1. UV-A content is extremely low and can be ignored.
2. UV-B content is negligible.
3. High blue light content may cause retinal damage. LED light with a color temperature below 3500K is safer.
4. Almost no near-infrared content, so it doesn't need to be considered.
LED white light is created by combining a blue LED chip with a yellow phosphor coating. This method allows for efficient and versatile lighting solutions.
While LED lighting offers many advantages over traditional sources, improper use can lead to "blue light hazard." This is particularly true for high-color-temperature LEDs, which emit more blue light and may increase the risk of retinal damage.
"Blue light hazard" is a public health issue. Product information should clearly state whether there is a risk. The best way to determine safety is through blue light radiation testing.
The higher the power of the LED product, the greater the blue light hazard. For products above 20W, it's important to consider the installation height—higher placement reduces the risk.
As color temperature decreases, so does the amount of blue light emitted. Low-power LEDs with a color temperature between 3500K and 2800K generally meet safety standards. LEDs with a color temperature above 6500K may have higher blue light exposure.
Color rendering also plays a role. Higher color rendering means more blue light absorption, which makes the LED safer. Therefore, high-color-rendering LEDs are preferred for health reasons.
Here are some recommendations:
1. For commercial lighting, choose LED white light with a color temperature below 6000K (up to 6500K maximum).
2. For office lighting, use a color temperature between 5000K and 3200K.
3. For home lighting, prefer LED lights with a power below 8W and a color temperature below 3500K.
4. Choose LEDs with high color rendering for general lighting.
5. For reading lamps, use LEDs with high color rendering and a color temperature below 3200K, with power under 6W.

Figure: Indoor Lighting Color Temperature Reference Map
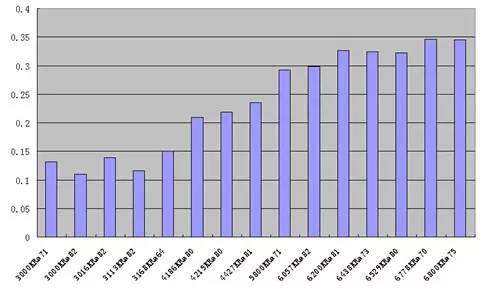
Figure: Blue Radiation Ratio of LED Illumination Sources (varies by manufacturer)
For assessing the blue light hazard on the retina, refer to the following table:
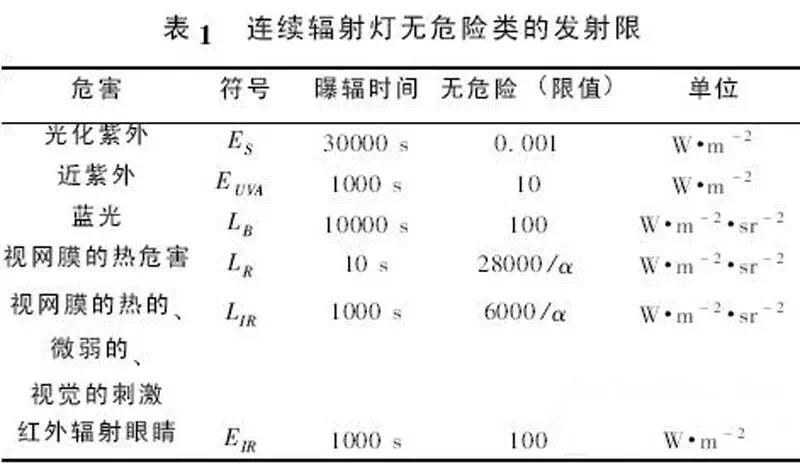
Figure: GB/T 20145-2006 Photobiosafety of Lamps and Lamp Systems, Hazard Limits for Radiation.
Tags: Popular Science | What Are the Effects of Different Light Sources on Health?
Ring Common Mode Inductor,UU Common Mode Inductor,Vertical Plug-in Common Mode Inductor,Power Line Common Mode Choke
Xuzhou Jiuli Electronics Co., Ltd , https://www.xzjiulielectronic.com



