Oxidation reduction potential, referred to as ORP or Eh. ORP as a comprehensive indicator of the environmental conditions of the medium (including soil, natural water, culture medium, etc.) has been used for a long time, which characterizes the relative degree of oxidative or reductive properties of the medium. The ORP measuring electrode can be made of various metals, such as nickel, copper, silver, iridium, platinum, gold, etc., which are composed of an ionic lattice structure, electrons can move inside the crystal lattice, and they also generate a potential difference due to the presence of the same kind of ions. . An ORP electrode is an electrode that can absorb or release electrons on the surface of a sensitive layer. The sensitive layer is an inert metal, usually made of platinum and gold.

The redox system used in water treatment is mainly the reduction of chromic acid and the oxidation of cyanide. If sodium disulfide or sulfur dioxide is added to the wastewater, the hexavalent chromium ion can be converted into a trivalent chromium. If chlorine or sodium hypochlorite is added, it can be used to oxidize cyanide, followed by hydrolysis of cyanogen chloride to form a cyanate salt. This chemical reaction process is called a redox reaction system. The redox potential is a measure of electron activity, which is similar to the method of measuring hydrogen ion activity.
Water disinfection and applicationThe redox electrode measures the disinfection effect on swimming pool water, mineral water and tap water. Since the bactericidal effect of coliforms in water is affected by the redox potential, the redox potential is a reliable indicator of water quality. If the redox potential value of pool water and mineral water is equal to or higher than 650 mv, it means that the bacteria content is acceptable.
Soil ORP changeObserve the dynamic changes of ORP in soil, etc.
For example, after rice paddy is planted with water, the redox status of the soil has changed drastically. There is a paddy soil viewed from the tillage layer and generally maintained at 450-650 mV before irrigation. After irrigation, the ORP drops rapidly. When the organic matter is decomposed, the ORP drops to minus 200mV to 100mV. When a large amount of fresh green manure is applied, it can even drop to minus 300mV. It will rise again in the future and is generally maintained at 0-200mV. Before the rice harvest, the soil dries and the ORP rises back above 450mV (extracted from Tianren, the physical chemistry of the paddy soil).
Other applicationsMarine exploration, bioengineering, environmental protection, brewing industry and other sectors of the national economy have been widely used.
The role of orp in sewage treatmentIn the early 1940s, practical ORP monitoring electrodes have been developed and applied to the control of aeration in sewage biological treatment. However, when an effective DO sensor was developed, the operator lost interest in ORP monitoring because the ORP was an environmental variable and its monitoring results were relatively difficult to reasonably explain. Until recently, when nutrients were removed as hot spots, people became interested in the research and application of ORP because DO sensors could not function in the anoxic and anaerobic regions of biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal processes, while ORP and other conventional and relatively simple Sensors provide useful information for process control and status assessment at a low cost.
In addition, based on 15 years of experience, Charpentier J. et al. pointed out that the actual measured ORP values ​​are consistent with the values ​​predicted by the electrochemical equilibrium theory. ORP data can also provide useful information on physical or biological activity in an aeration tank (as shown in Figure 2).
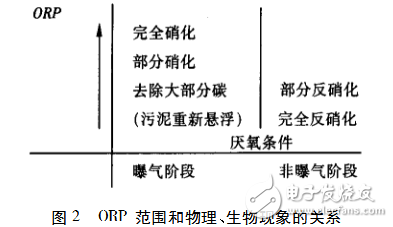
Figure 2 shows the sequence in which dissolved contaminants are removed. The carbon, sulfur and nitrogen compounds in the sewage are converted by redox reaction. The carbon compounds have the strongest reduction. Most of the carbon sources are removed in the lower ORP range during the aeration phase, and the rest are floc. Adsorption and continued slow oxidation, while nitrogen compounds are most difficult to oxidize. It has been confirmed that the ORP value (platinum/AgCl electrode) is close to +200 mV at the end of aeration during denitrification, the ORP value (platinum/AgCl electrode) is close to -130 mV when a large amount of iron salt is added, and the range of occurrence of hydrogen sulfide is ORP (platinum) /AgCl electrode) is -250~-300mV.
The ORP value is related to the energy released by the biochemical reaction in the activated sludge process. Thus the ORP value increases or decreases with the concentration of electron acceptors (oxygen, nitrates, sulfates, etc.) and reactants and products, however this change is not proportional to the concentration and is proportional to the logarithm of the concentration. A large number of experiments and actual operational studies have shown that there is a good correlation between ORP and NOX, phosphorus and ammonia nitrogen. Some researchers have proposed a control method based on the absolute value of ORP or detecting the inflection point of ORP curve. Others tend to use ORP combined time setting and DO, pH or ammonia sensor to control the aeration time and optimize the lower limit of ORP value to judge the organic load. And microbial proliferative capacity involved in denitrification.
The variation of ORP value can be used to optimize the nitrification and denitrification cycles to ensure denitrification and respond to changes in organic matter concentration. The blower is activated to prevent the release of H2S before the strong reducing organic matter begins to reduce the sulfate to sulfide. NO-3-N in the phosphorus system can also help to add chemical treatments for special treatment to activated sludge (such as adding iron salt to remove phosphorus, chlorine to return sludge to prevent and inhibit sludge expansion, etc.) ). The ORP signal change can also determine the abnormal operating conditions of the treatment plant, such as aeration device failure, impact load, and the like. At present, ORP has been successfully used for aeration and agitation time control in denitrification in anoxic process such as SBR and biodenitro.
In the anaerobic biological treatment process, ORP is also an important control parameter, which can be used to judge and control the biological anaerobic nutrient metabolism pathway and achieve the purpose of controlling metabolites, so that the whole biological system can develop in a precise and controllable direction. In the case of ethanol type fermentation (ORP is around -250 mV), it can be controlled by adding oxidizing or reducing substances (such as iron powder) to the water.
As ar wire automotive Tape Harness Tape,the Car Harness Tape can create a moisture seal and waterproof at wiring harness in automobile industry. And the Automotive Tape will not dry out. Excellent insulation and adhesive properties makes Wire Tape a famours product in our factory.
Compared with Cloth Tape Automotive,our ar wire automotive Tape have the good property of heat resistant, in other words,it is a heat resistant Harness Tape
Automotive Tape,Cloth Tape Automotive,Car wire automotive Tape,Car Harness Tape,heat resistant Harness Tape
CAS Applied Chemistry Materials Co.,Ltd. , https://www.casac1997.com